Offshore Aquaculture Solutions
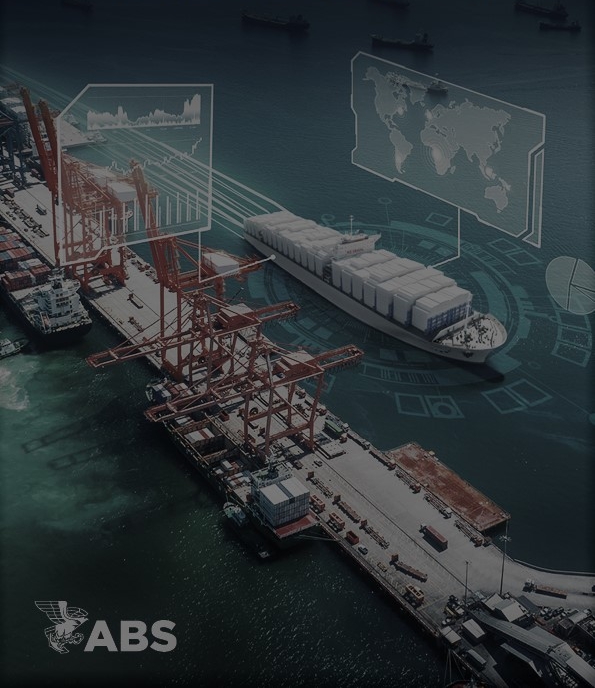
Aquaculture, also known as mariculture, is evolving as operators seek new opportunities offshore. The shift from inshore to offshore locations is driven by the need for expanded production space and reduced exposure to pollution, rising costs and competition for shoreline access.
To support this transition, ABS published the Guide for Building and Classing Aquaculture Installations. This guide applies to a range of installation types, including spar-type, column-stabilized, ship-shaped floating fish farms and non-buoyant configurations.
The guide outlines classification requirements for the design, construction, installation and survey of non-self-propelled, sited aquaculture installations. It focuses on three core components: hull structure, mooring systems or foundations, and onboard machinery and systems not directly part of the aquaculture process. Vessels meeting these requirements may receive the notations Fish Farm Installation, Manned or Fish Farm Installation, Unmanned, accordingly.
ABS also published the Guide for Building and Classing Aquaculture Service Vessels, which addresses classification for support vessels, pellet carriers, live and refrigerated fish carriers, harvest units and processing vessels. Vessels that meet the criteria may be assigned notations such as ASV-Support, ASV-Fish Pellet, or ASV-Live Fish.
ABS has contributed to multiple aquaculture installation projects, applying tailored approaches to address global performance, structural design, mooring arrangements and stability characteristics unique to each installation.
Connect with ABS
For guidance on aquaculture installations or service vessels, reach out to the ABS team at GlobalOffshore@eagle.org. Our team is available to support your offshore initiatives and help navigate classification requirements.